A lake that hides a 500-year-old secret
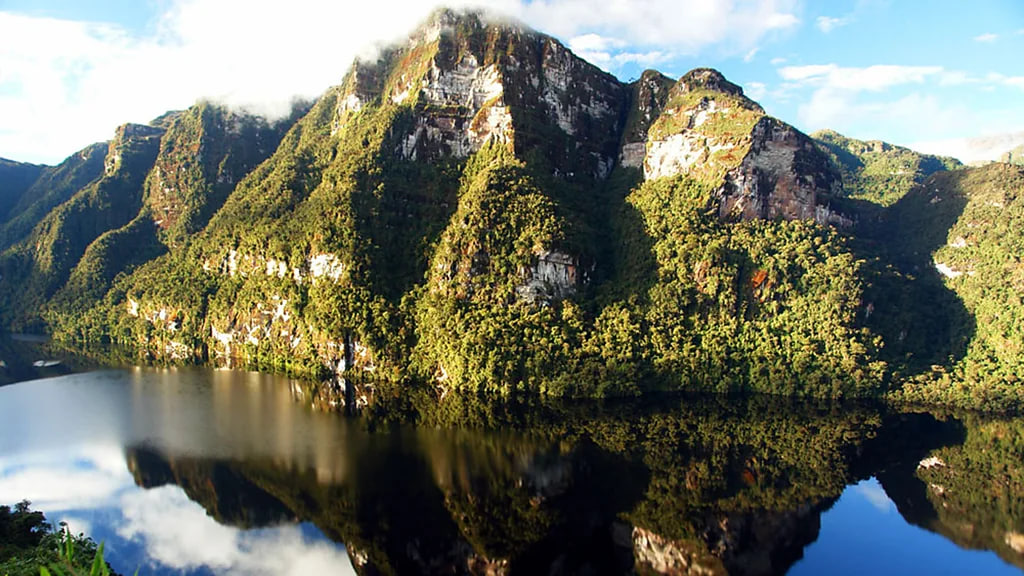

Laguna de los Condores is one of the country’s most important Inca sites – but only 150 people trek to this remote spot each year.
High in the remote northwestern Andes is a stunning mountain lake that’s held a secret for more than 500 years.
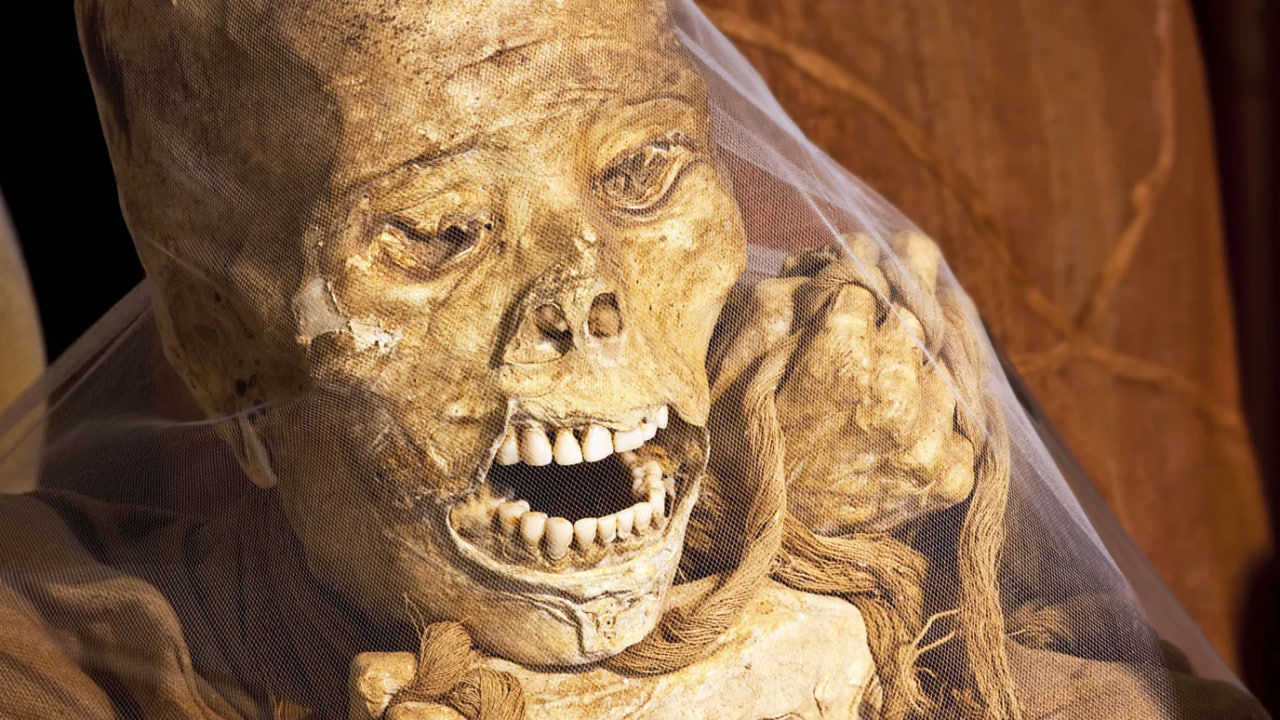
Laguna de los Condores, located in northern Peru’s remote Chachapoyas region, became one of the country’s most important Inca sites in 1997 when archaeologists discovered hundreds of mummies in a mausoleum built into the steep surrounding cliff-face. Those bodies are now conserved in the nearby Leymebamba Museum, but thousands more preserved corpses are thought to remain in 17 other mausoleums hidden in the jungle-covered mountains – still unexcavated due to the high cost of archaeology work in this remote region.
 Krista Eleftheriou
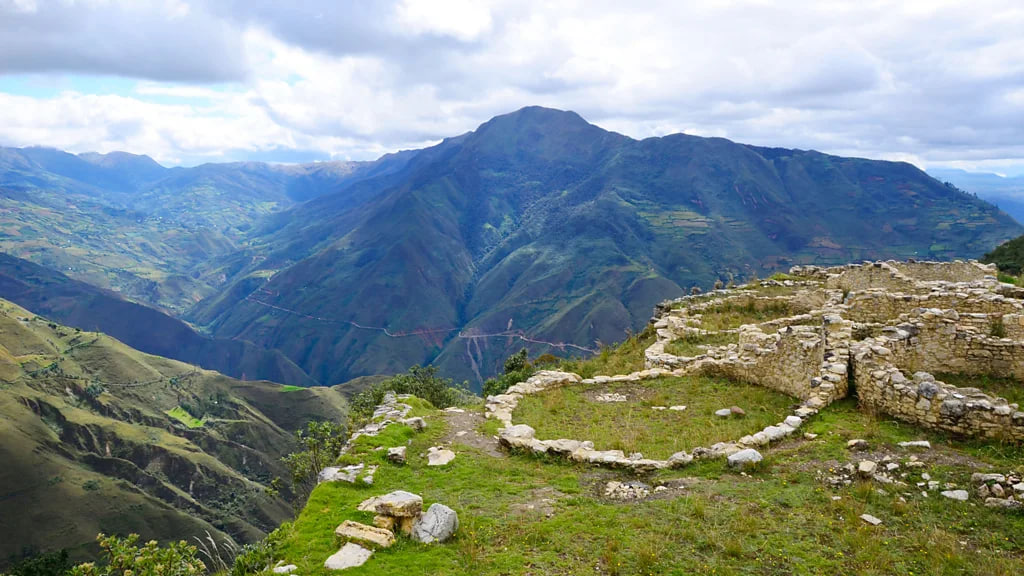
Krista EleftheriouIncredibly, just 150 people trek to this little-known spot each year. But that looks set to change with the construction of Peru’s first cable car to the nearby archaeology site of Kuelap. Located just 80km north of Laguna de los Condores, Kuelap’s mountain top ruins, known as “the Machu Picchu of the north”, were a religious and political centre for the pre-Inca Chachapoyan people. The July 2016 opening of the cable car – along with plans to start commercial flights to the region– means that the coming months and years will see increasing numbers of visitors to the entire Chachapoyas area.

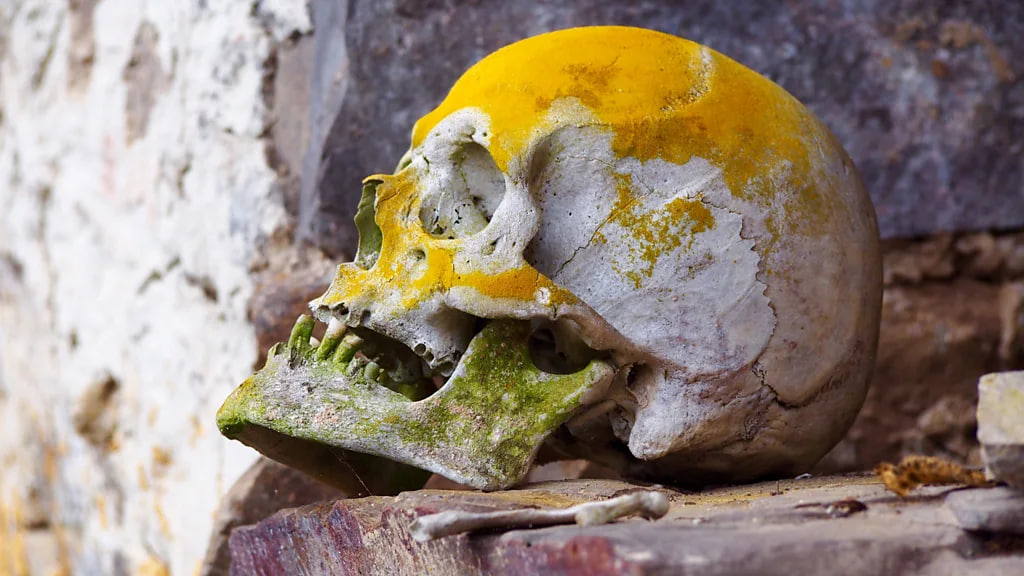
According to bio-anthropologist Dr Sonia Guillen, Peru’s leading expert on mummies, the Laguna de los Condores excavation is one of the most significant discoveries relating to the Inca period in South America, as it’s one of only two known large Inca burial sites to have escaped destruction by Spanish conquistadors.
“The finding was sort of a miracle,” Guillen said when I met her at the Leymebamba Museum. “These mummies are very significant, because they are the first to show us how the Incas prepared their dead in the royal way. They cured the skin to preserve it and made it into leather and they extracted the organs through the anus.”
 Krista Eleftheriou
Krista EleftheriouThe mummified bodies were then wrapped in woven textiles and surrounded with artefacts and offerings, such as pots, feathers, woven baskets and quipus: knotted Inca tools that recorded stories and accounting.
She explained that the Laguna de los Condores mummies likely held high positions in Inca society, due to the elaborate burial process and the lack of wear and tear on the bones usually associated with manual labour. One of the reasons the Inca mummified their elite was to keep them connected with the community.
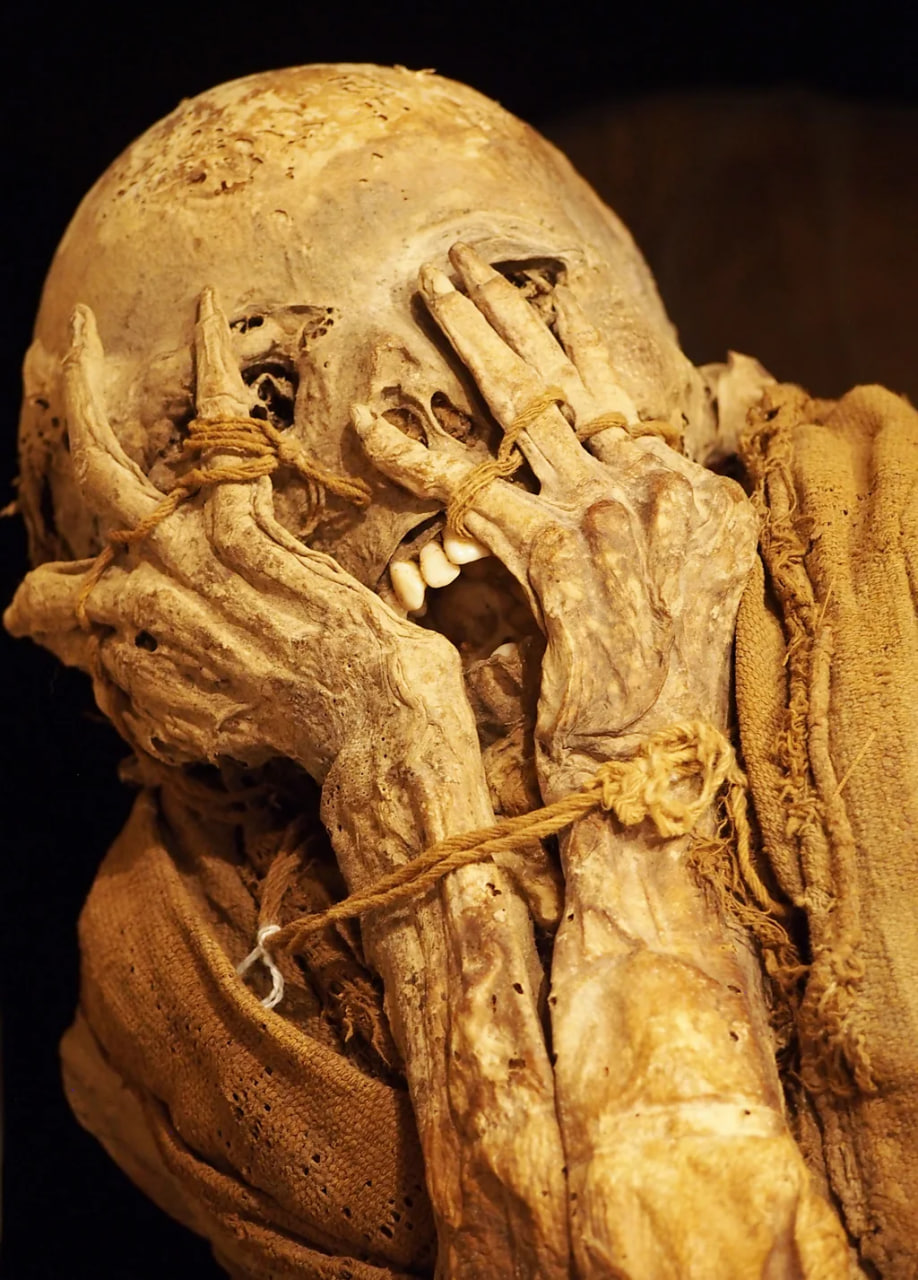
“The Incas revered their royal dead because they were still very much part of the world of the living,” Guillen said. “The Inca mummy participated in meetings, still held property and made decisions.”
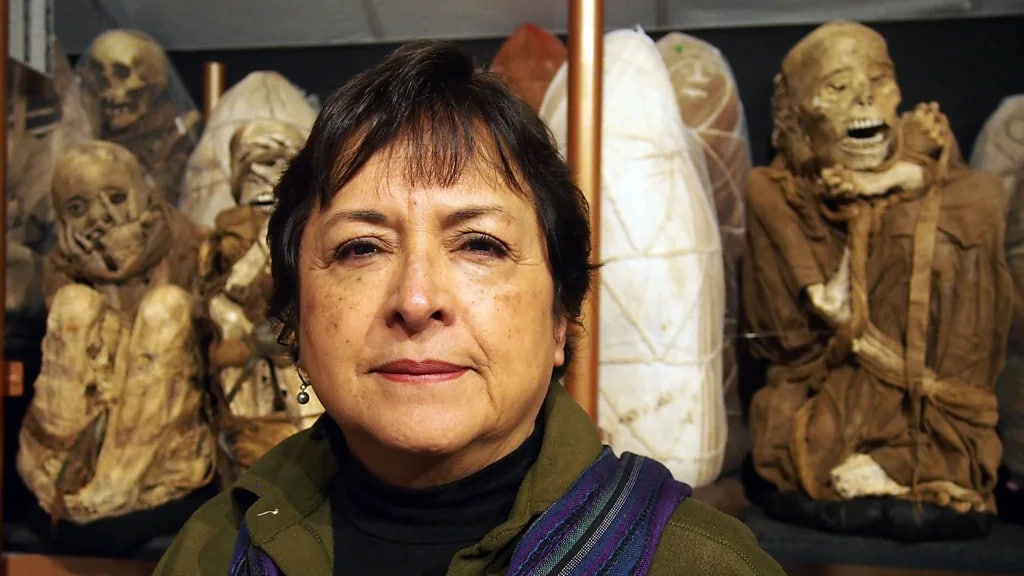
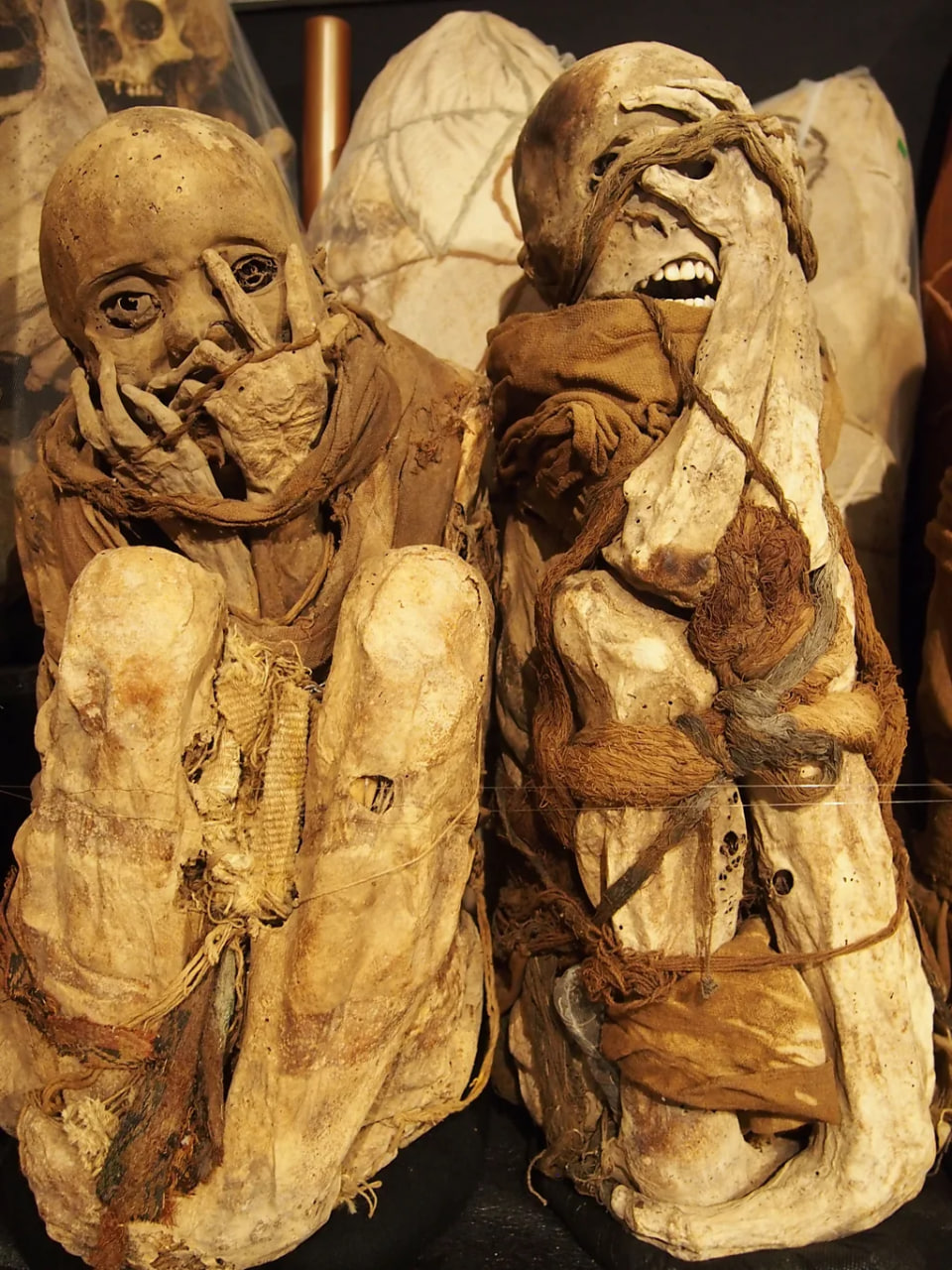
Guillen took me around me the rows of mummies that lined the museum shelves, some still wrapped in the traditional funeral dressing, others with their skeletons visible, their bodies arranged into the foetal position.
“Each mummy can tell you a story. This guy died when he was 17 or 18 years old; we know that because of his teeth,” she said, pointing out one of the bodies. “He was a bird catcher because his body is wrapped in nets.” Feathers were of high value in Inca society and a bird catcher was a prestigious role.

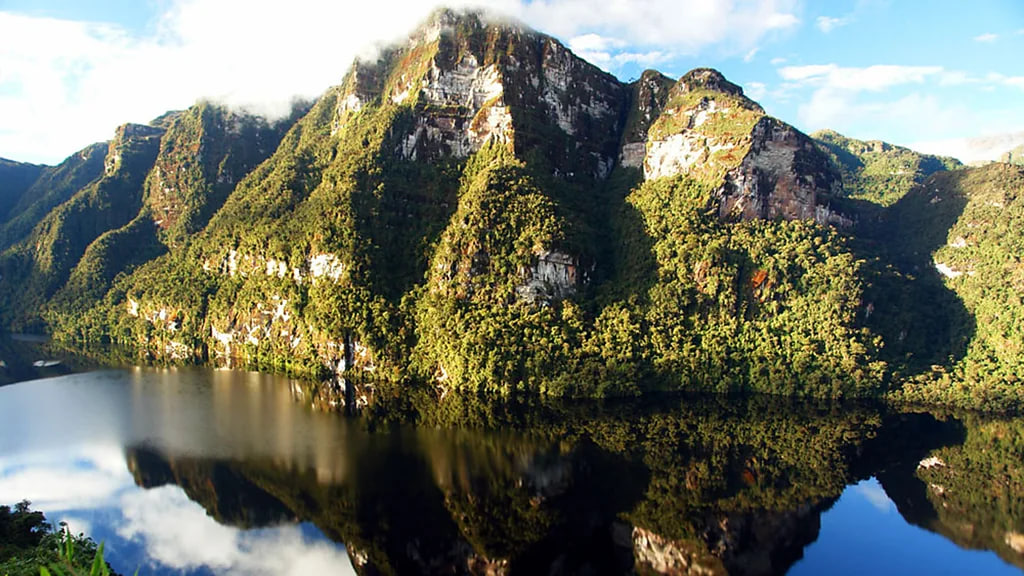
I was so intrigued by her tales that I decided to hike the 10-hour track from the village of Leymebamba to Laguna de los Condores, passing through dense Amazon jungle and muddy rolling savanna along the way. The view that greeted me was spectacular. Draped in clouds, soaring mountains rose up from the lake, waterfalls flowed down the sheer face and everything reflected in the dark lagoon water.
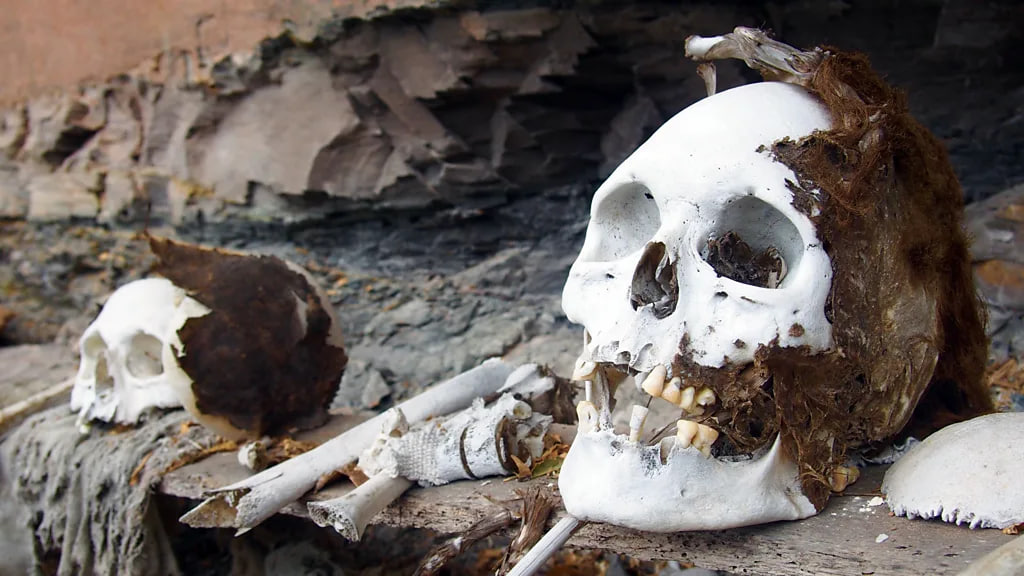
After a night in a mud-floor farmhouse, my guide Eilen and I crossed the lake in a small boat. Eilen fished, catching trout to make a dinner of traditional Andean trucha (fried fish in a lemon or cream sauce). He pointed out the location near the base of the mountain where two mummies had been found. Only the wooden platform that held the bodies remained; the mummies have since been removed for conservation. But it was these two mummies that had provided the first clues that this was no ordinary body of water.
 Carlo M Inga
Carlo M IngaAn hour later we reached the opposite side of the lagoon and started the steep, muddy hike through thick jungle. With a machete in hand, Eilen carved a track and we passed under waterfalls and climbed ladders left behind by the archaeologists. On our arrival, we found several painted buildings where the mummies were originally housed. There were scattered bones and skulls on the ground and ancient artwork of animals and symbols painted on the walls.
According to Guillen, burial sites such as the Laguna de Los Condores mausoleums were crucial to the Incas’ success in taking control of the region, culture and the people, as they replaced the Chachapoyan way of burial with the Inca tradition of mummification.
 Krista Eleftheriou
Krista Eleftheriou“When the Incas conquered this area, they replaced the funerary pattern. They emptied the mausoleums [of the pre-Inca Chachapoya dead] and conquered their spirit by conquering their sacred places,” she said.
I sat among the mausoleum ruins, looking out over the lake towards the village ruins on the opposite side where the Inca, and before them the Chachapoyan people, had lived. A waterfall flowed down the cliff in front me. I thought of the people that had lived here, wondering how they had managed to construct buildings in such steep jungle-covered cliffs.
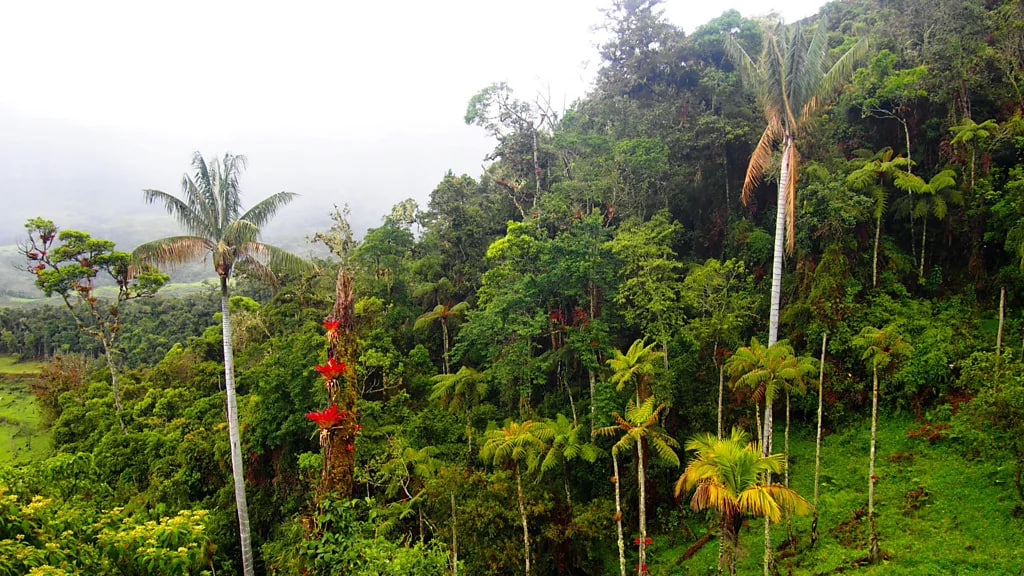

It seemed phenomenal that such a beautiful place that was once a thriving community for more than 500 years could be abandoned during the Spanish conquest, reclaimed by nature and lie hidden for half a millennium.
I couldn’t help but wonder what else was hidden in the mountains.
 Frans Lemmens/Alamy
Frans Lemmens/Alamy







