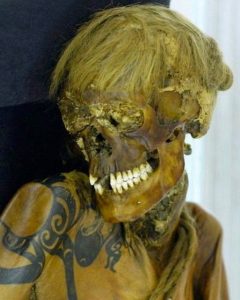
Denisovans are an extinct species of hominid and a close relative to modern humans. They’re a recent addition to the human family tree—scientists first identified Denisovan remains from a cave in Siberia in 2010. Denisovans may have ranged from Siberia to Southeast Asia during the last Ice Age. DNA evidence suggests Denisovans are related to both Neanderthals and modern humans, and may have interbred with both.
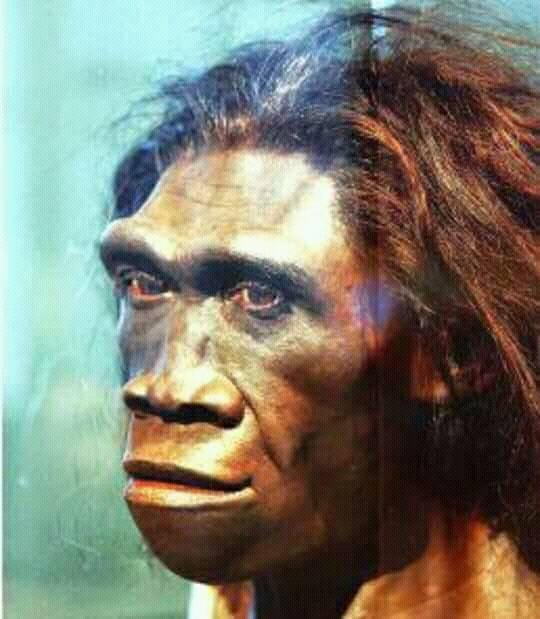

Denisovans share a common ancestor with both modern humans and Neanderthals. This common ancestor, called Homo heidelbergensis, most likely lived in Africa.
Between 300,000 and 400,000 years ago, one group of Homo heidelbergensis left Africa. They expanded into Eurasia and then split: Those that moved west into Europe evolved into Neanderthals. The ones that moved east into Asia became Denisovans.
The human ancestors that remained in Africa evolved into our own species—Homo sapiens. Modern humans and Denisovans likely met for the first time in Eurasia some 40,000 to 60,000 years ago, after Homo sapiens began their own migration out of Africa.

Denisovan Discovery
Denisovans are a relatively recent discovery: In 2008, Russian paleoanthropologists exploring Siberia’s Denisova Cave—located in the Altai Mountains along Russia’s southern border with China and Mongolia—found a tiny, pea-sized fragment of finger bone.
They determined the fossilized pinkie bone had belonged to a young girl between the ages of about five and seven when she died roughly 40,000 years ago. Cold weather in the Siberian cave helped to preserve ancient DNA.
In 2010, a group of scientists led by Svante Paabo of the Max Planck Society in Germany extracted DNA from the tiny bone fragment.
Scientists sequenced the girl’s genome and compared it to the genomes of modern humans and Neanderthals—two other hominin species known to be living in Eurasia at the time. Studies showed that the girl was genetically similar to both Neanderthals and Homo sapiens, but distinct enough to be considered a new species of human.
The researchers named the archaic humans Denisovans after the cave in Siberia where the fossil was discovered. Scientists have since discovered fossilized teeth from three other Denisovan individuals—all from inside Denisova Cave.
Denisovan DNA
Since very few Denisovan fossils have been found, most of what we know about the extinct humans comes from their DNA.
It’s not clear when exactly Denisovans evolved—or when they went extinct—but DNA evidence suggests they were living in Asia at least 80,000 years ago. They may have had dark skin, dark hair and dark eyes. The Denisovan genome appears to have low genetic diversity, which means their population may never have been very large.
Researchers believe that modern human ancestors may have interbred with Denisovans. Denisovan DNA can be found in the human genome.
Melanesians
Some present-day East Asian groups, in particular Melanesians, may have inherited up to five percent of their genetic material from Denisovans. Melanesians are Pacific Islanders native to a region spanning from Papua New Guinea to Fiji.
Scientists theorize that Denisovans living in East Asia may have interbred with the ancestors of present day Melanesians before those humans crossed the Pacific Ocean to reach Papua New Guinea approximately 45,000 years ago.
Tibetans and Han Chinese have traces of Denisovan DNA in their genomes too. In 2014, researchers discovered that ethnic Sherpas likely inherited from Denisovans a “super athlete” gene variant that helps them breathe easily at high altitudes.
Baffling 400,000-Year-Old Clue to Human Origins
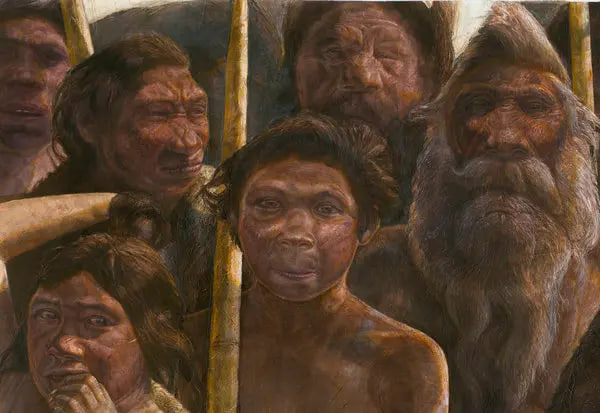

Scientists have found the oldest DNA evidence yet of humans’ biological history. But instead of neatly clarifying human evolution, the finding is adding new mysteries.
In a paper in the journal Nature, scientists reported Wednesday that they had retrieved ancient human DNA from a fossil dating back about 400,000 years, shattering the previous record of 100,000 years.
The fossil, a thigh bone found in Spain, had previously seemed to many experts to belong to a forerunner of Neanderthals. But its DNA tells a very different story. It most closely resembles DNA from an enigmatic lineage of humans known as Denisovans. Until now, Denisovans were known only from DNA retrieved from 80,000-year-old remains in Siberia, 4,000 miles east of where the new DNA was found.
The mismatch between the anatomical and genetic evidence surprised the scientists, who are now rethinking human evolution over the past few hundred thousand years. It is possible, for example, that there are many extinct human populations that scientists have yet to discover. They might have interbred, swapping DNA. Scientists hope that further studies of extremely ancient human DNA will clarify the mystery.
“Right now, we’ve basically generated a big question mark,” said Matthias Meyer, a geneticist at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, and a co-author of the new study.
Hints at new hidden complexities in the human story came from a 400,000-year-old femur found in a cave in Spain called Sima de los Huesos (“the pit of bones” in Spanish). The scientific team used new methods to extract the ancient DNA from the fossil.
“This would not have been possible even a year ago,” said Juan Luis Arsuaga, a paleoanthropologist at Universidad Complutense de Madrid and a co-author of the paper.
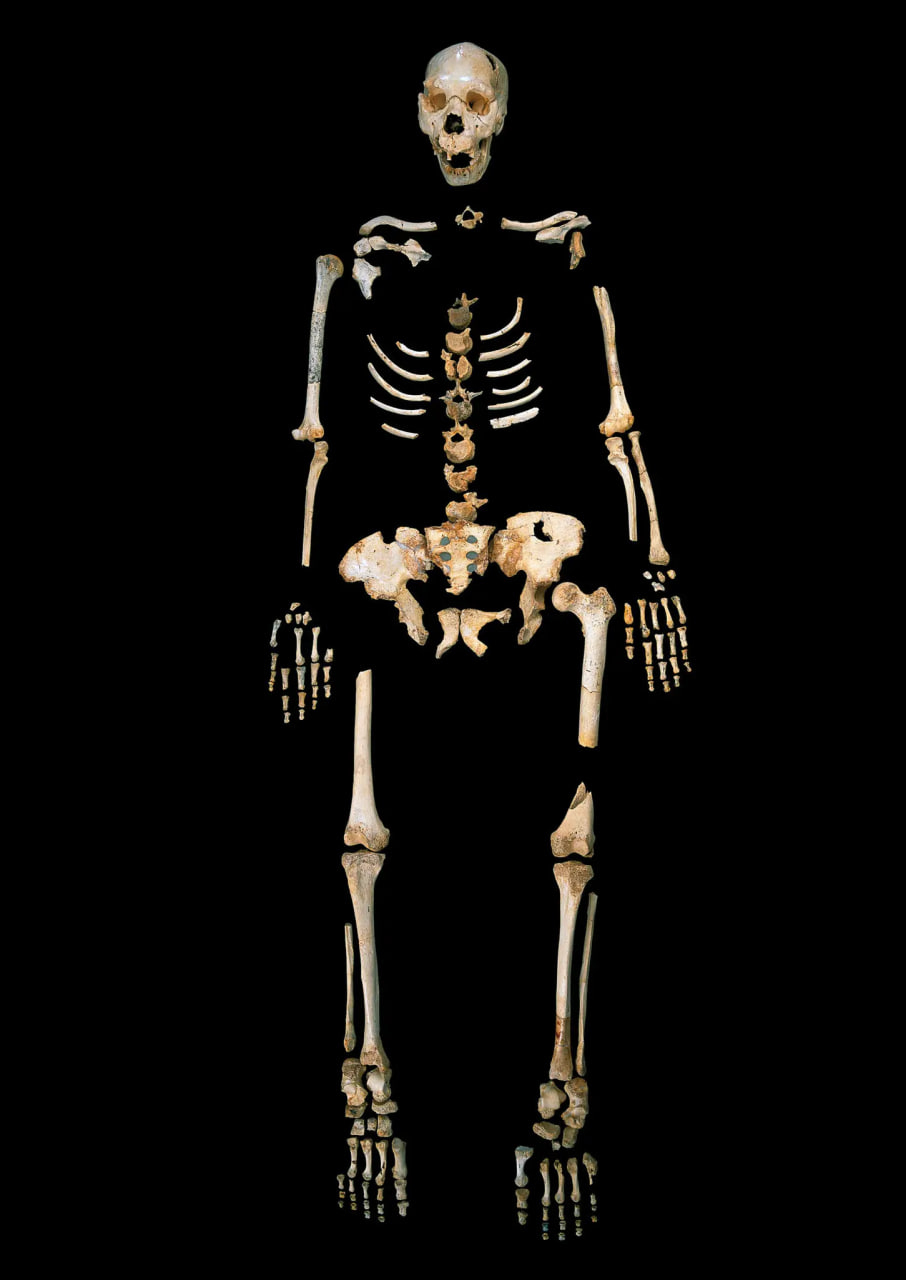
The skeleton of a hominin recovered from Sima de los Huesos.Credit…Javier Trueba, Madrid Scientific Films
Finding such ancient human DNA was a major advance, said David Reich, a geneticist at Harvard Medical School who was not involved in the research. “That’s an amazing, game-changing thing,” he said.
Since the 1970s, Spanish scientists have brought out a wealth of fossils from the cave dating back hundreds of thousands of years. “The place is very special,” said Dr. Arsuaga, who has found 28 nearly complete skeletons of humans during three decades of excavations.
Based on the anatomy of the fossils, Dr. Arsuaga has argued that they belonged to ancestors of Neanderthals, which lived in western Asia and Europe from about 200,000 to 30,000 years ago.
When Dr. Meyer and his colleagues drilled into the femur, they found ancient human DNA inside, just as they had hoped.
“Our expectation was that it would be a very early Neanderthal,” Dr. Meyer said.
But the DNA did not match that of Neanderthals. Dr. Meyer then compared it to the DNA of the Denisovans, the ancient human lineage that he and his colleagues had discovered in Siberia in 2010. He was shocked to find that it was similar.
“Everybody had a hard time believing it at first,” Dr. Meyer said. “So we generated more and more data to nail it down.”
The extra search confirmed that the DNA belonged on the Denisovan branch of the human family tree.
The new fnding is hard to reconcile with the picture of human evolution that has been emerging based on fossils and ancient DNA. Denisovans were believed to be limited to East Asia, and they were not thought to look so Neanderthal-like.

The thigh bone of a 400,000-year-old hominin from Sima de los Huesos, Spain.Credit…Javier Trueba, Madrid Scientific Films
Based on previously discovered ancient DNA and fossil evidence, scientists generally agreed that humans’ direct ancestors shared a common ancestor with Neanderthals and Denisovans that lived about half a million years ago in Africa.
Their shared ancestors split off from humans’ lineage and left Africa, then split further into the Denisovans and Neanderthals about 300,000 years ago. The evidence suggested that Neanderthals headed west, toward Europe, and that the Denisovans moved east.
Humans’ ancestors, meanwhile, stayed in Africa, giving rise to Homo sapiens about 200,000 years ago. Humans then expanded from Africa into Asia and Europe about 60,000 years ago. They then interbred not only with Neanderthals, but with Denisovans, too. Later, both the Denisovans and Neanderthals became extinct.
“Now we have to rethink the whole story,” Dr. Arsuaga said.
Dr. Arsuaga doubts that Denisovans were spread out across so much of the Old World, from Spain to Siberia, masquerading as Neanderthals.
One alternative explanation is that the humans of Sima de los Huesos were not true Neanderthals, but belonged to the ancestors of both Denisovans and Neanderthals.
It is also possible that the newly discovered DNA was passed to both Neanderthals and Denisovans, but eventually disappeared from Neanderthals, replaced by other variants.
“It got lost in one lineage but made its way in the other,” suggested Jean-Jacques Hublin, a Max Planck paleoanthropologist who was not involved in the research.
Beth Shapiro, an expert on ancient DNA at the University of California, Santa Cruz, favors an even more radical possibility: that the humans of Sima de los Huesos belong to yet another branch of humans. They might have been a species called Homo erectus, which originated about 1.8 million years ago and became extinct within the last few hundred thousand years.

Carl ZimmerCredit…Earl Wilson/The New York Times
“The more we learn from the DNA extracted from these fossils, the more complicated the story becomes,” Dr. Shapiro said.
This complicated story has come to light only because of advances over the past 20 years in retrieving ancient DNA.
When an organism dies, its DNA breaks down into smaller and smaller fragments, while also becoming contaminated with the DNA of other species like soil bacteria. So piecing the fossil DNA together is a bit like putting together a jigsaw puzzle created by a sadist.
In 1997, Svante Paabo of the Max Planck Institute and his colleagues, who had pioneered the techniques for retrieving DNA fragments, published a snippet of DNA from a Neanderthal fossil dating back about 40,000 years. They and other scientists then built on this success by searching for bits of DNA from other Neanderthals.
In 2006, a team of French and Belgian researchers obtained a fragment of Neanderthal DNA dating back 100,000 years, which until now held the record for the oldest human DNA ever found.
Meanwhile, using improved methods, Dr. Paabo, Dr. Meyer and their colleagues assembled a rough draft of the entire Neanderthal genome in 2010.
That discovery shed light on how Neanderthals and humans’ ancestors split from a common ancestor hundreds of thousands of years ago. It also revealed that Neanderthals and humans interbred about 50,000 years ago.
Around the same time as that discovery, Russian collaborators sent the Max Planck team 80,000-year-old fossils they had found in a cave in Siberia called Denisova. When the German scientists sequenced the entire genome from the finger bone of a girl, it turned out to be neither human nor Neanderthal, but from a separate lineage, which Dr. Paabo and his colleagues named Denisovans.
Dr. Meyer is hopeful that he and his colleagues will be able to get more DNA from the Spanish fossil, as well as other fossils from the site, to help solve the puzzle they have now stumbled across. “It’s extremely hard to make sense of,” Dr. Meyer said. “We still are a bit lost here.”