
Researchers were initially surprised to find the remains of two baby girls inside the Boy King’s ancient tomb but later analysis has revealed much about their tragic deaths.
Tutankhamun: Expert discusses archaeologist Howard Carter
Tutankhamun ruled Ancient Egypt over 3,300 years ago for just nine years.

The shortest ruling pharaoh in Egyptian history, the Boy King was just eight or nine when he took the throne from his father, Akhenaten.
Egyptologists aren’t entirely sure why he died so young but believe it was likely from complications caused by a broken leg, made worse after he contracted malaria.

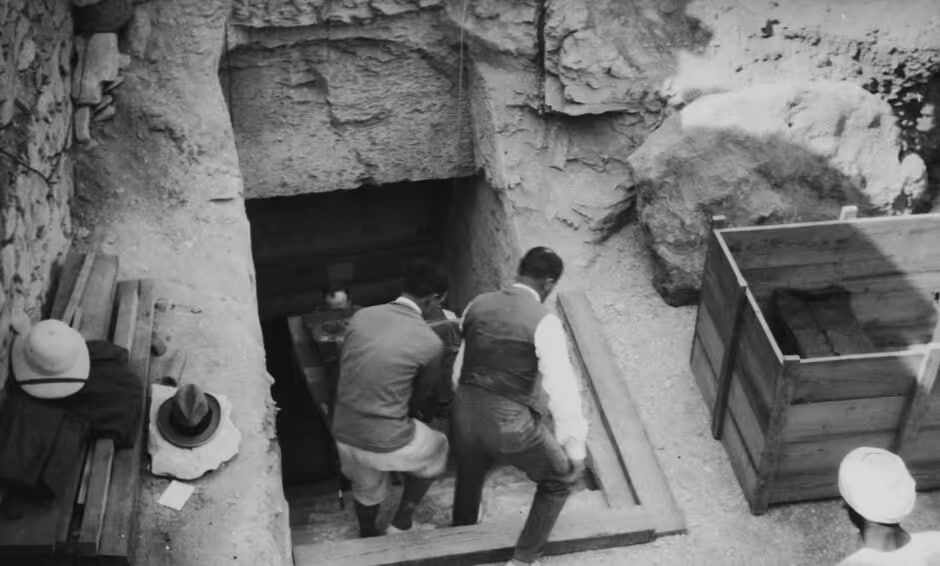
While archaeologists and grave robbers discovered and learned about many of Egypt’s great pharaohs, little was known about Tutankhamun until 1923 when British Egyptologist Howard Carter discovered his tomb.
He came across a treasure trove of priceless relics and artefacts, and one completely unexpected find — the remains of two baby girls, perfectly preserved due to mummification.
The Pharaoh’s Daughters
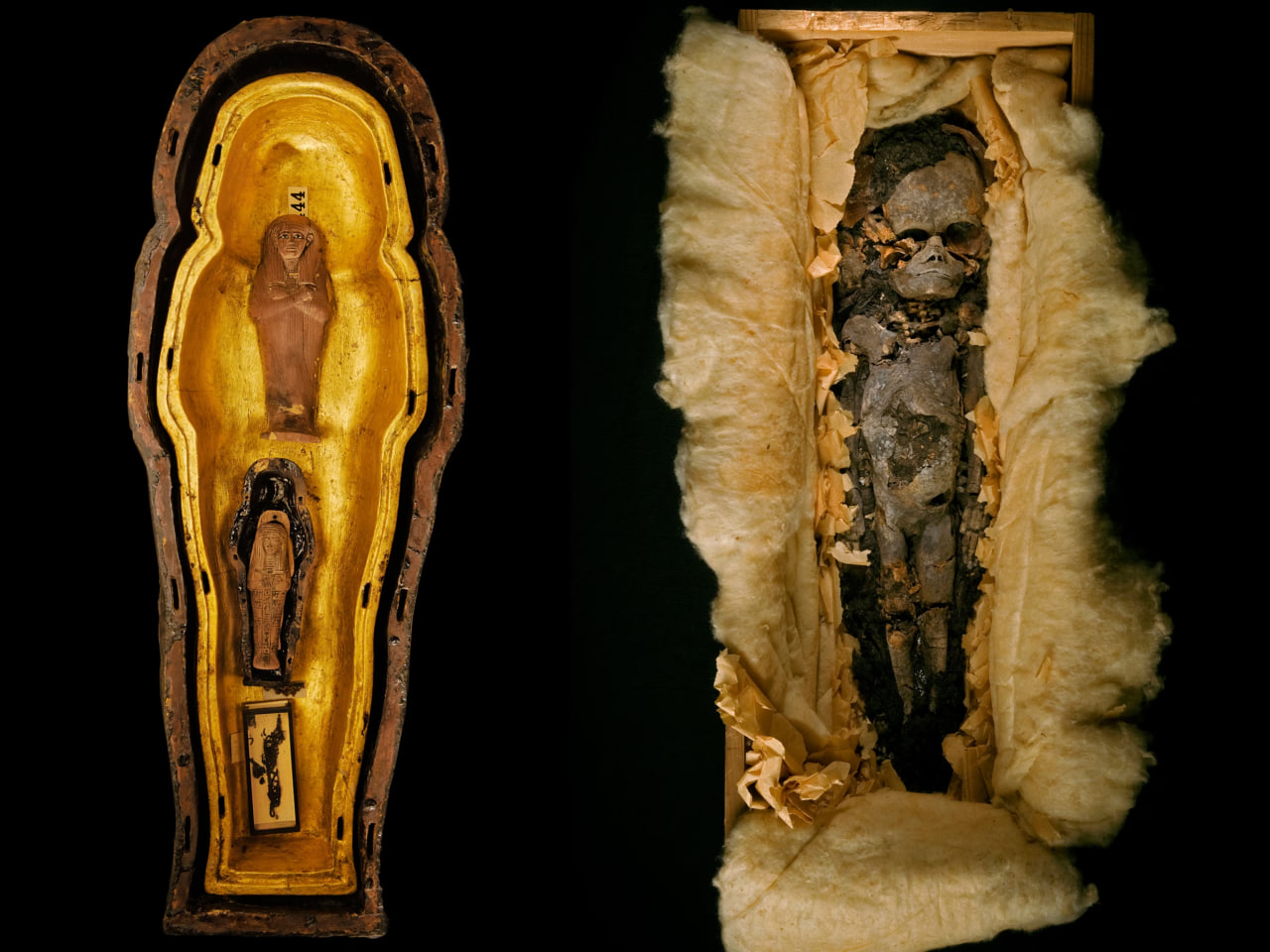

Mummy 317a (left) and Mummy 317b (right)
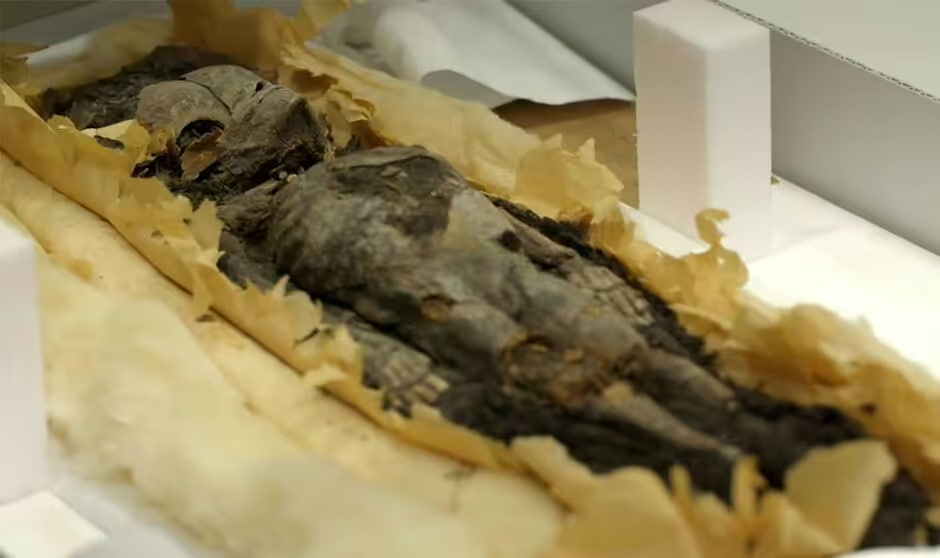
For three years after his 1922 discovery of King Tutankhamun’s tomb, archaeologist Howard Carter did not think much about an undecorated wooden box that turned out to contain two small resin-covered coffins, each of which held a smaller gold-foil-covered coffin. Inside these coffins were two tiny mummies. Preoccupied, Carter numbered the box 317 and did little to study it or its contents, only unwrapping the smaller of the two mummies, which he called 317a. The larger mummy he called 317b. The mummies were not carefully examined until 1932, when they were autopsied and photographed, at which time they were identified as stillborn female fetuses. But the most recent work on these two tiny girls, undertaken by radiologist Sahar Saleem of Cairo University, tells more of their story.
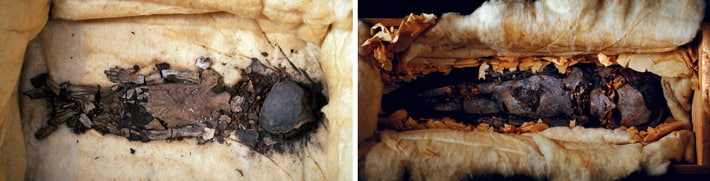
A decade ago, as head radiologist of the Egyptian Mummy Project, Saleem CT scanned the two fetuses, the first time any mummified fetus was studied using this technology. Though there is no evidence of the babies’ personal names—they are identified only by gold bands on the coffins calling them Osiris, the Egyptian god of the dead—they were, in fact, the daughters of Tutankhamun and his wife, Ankhesenamun, and were buried alongside their father after his death. Although both mummies were badly damaged, Saleem found that the girls died at 24 and 36 weeks’ gestation. It was previously known that the older girl, 317b, had had her organs removed as was typical to prepare the deceased for mummification. Saleem found an incision used to remove the organs on the side of 317a, as well as packing material of the sort placed under the skin of royal mummies to make them appear more lifelike. This contradicted the long-held belief that, unlike her sister, the younger girl had not been deliberately mummified.
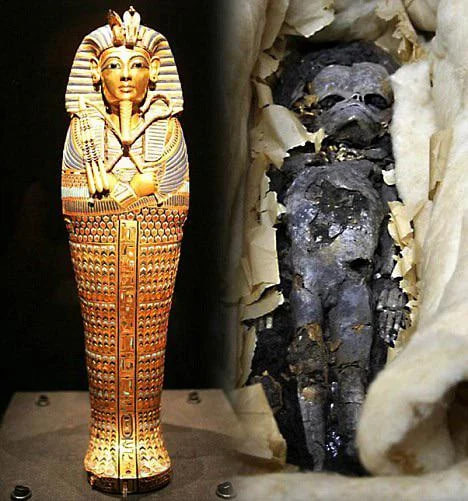

Similarly, by scanning the mummies, Saleem was able to definitively disprove previous claims that the girls had suffered from congenital abnormalities such as spina bifida. “They got it wrong,” she says. “The damage to their skeletons is a result of postmortem fractures and poor storage. For example, 317b’s elongated head is not a result of cranial abnormalities as has previously been said, but because she has a broken skull.” For Saleem, though, what she has learned about Tutankhamun’s daughters goes beyond these scientific questions. “I try to feel the person as a human in their journey of life,” she says. “Regardless of their age at death, Tut’s daughters were seen as worthy of receiving the most expert mummifications, of a royal burial with their father, and of an afterlife.”








