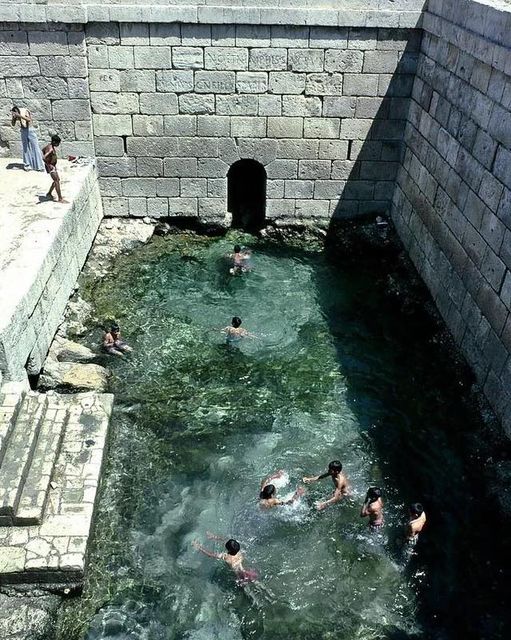
Nestled within the arid landscapes of Tunisia lies a hidden gem from antiquity – the Roman pools of Gafsa. Dating back to the 2nd century BCE, these remarkable structures serve as a testament to the ingenuity and engineering prowess of the ancient Romans. Despite the passage of centuries, the pools continue to captivate visitors with their grandeur and historical significance. In this blog post, we embark on a journey to explore the history, architecture, and cultural significance of the Roman pools of Gafsa, shedding light on their enduring legacy in the modern world.
The Architectural Marvels of Ancient Rome
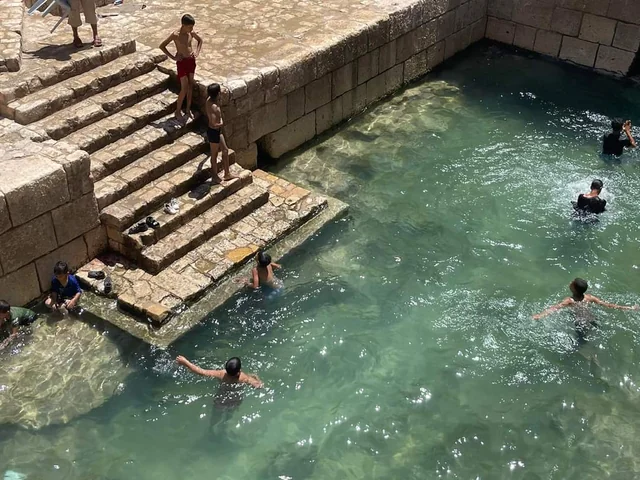

Constructed during the height of the Roman Empire, the pools of Gafsa stand as architectural marvels, showcasing the Romans’ mastery of engineering and hydrology. Spanning an impressive five meters in depth, these pools were meticulously crafted to harness the natural hot springs that flow beneath the earth’s surface. The Romans ingeniously channeled these thermal waters into the pools, creating serene and inviting bathing environments for both leisure and therapeutic purposes. With their precise construction and durable materials, the pools have withstood the test of time, offering a glimpse into the sophisticated infrastructure of ancient Rome.
Cultural Significance and Historical Context
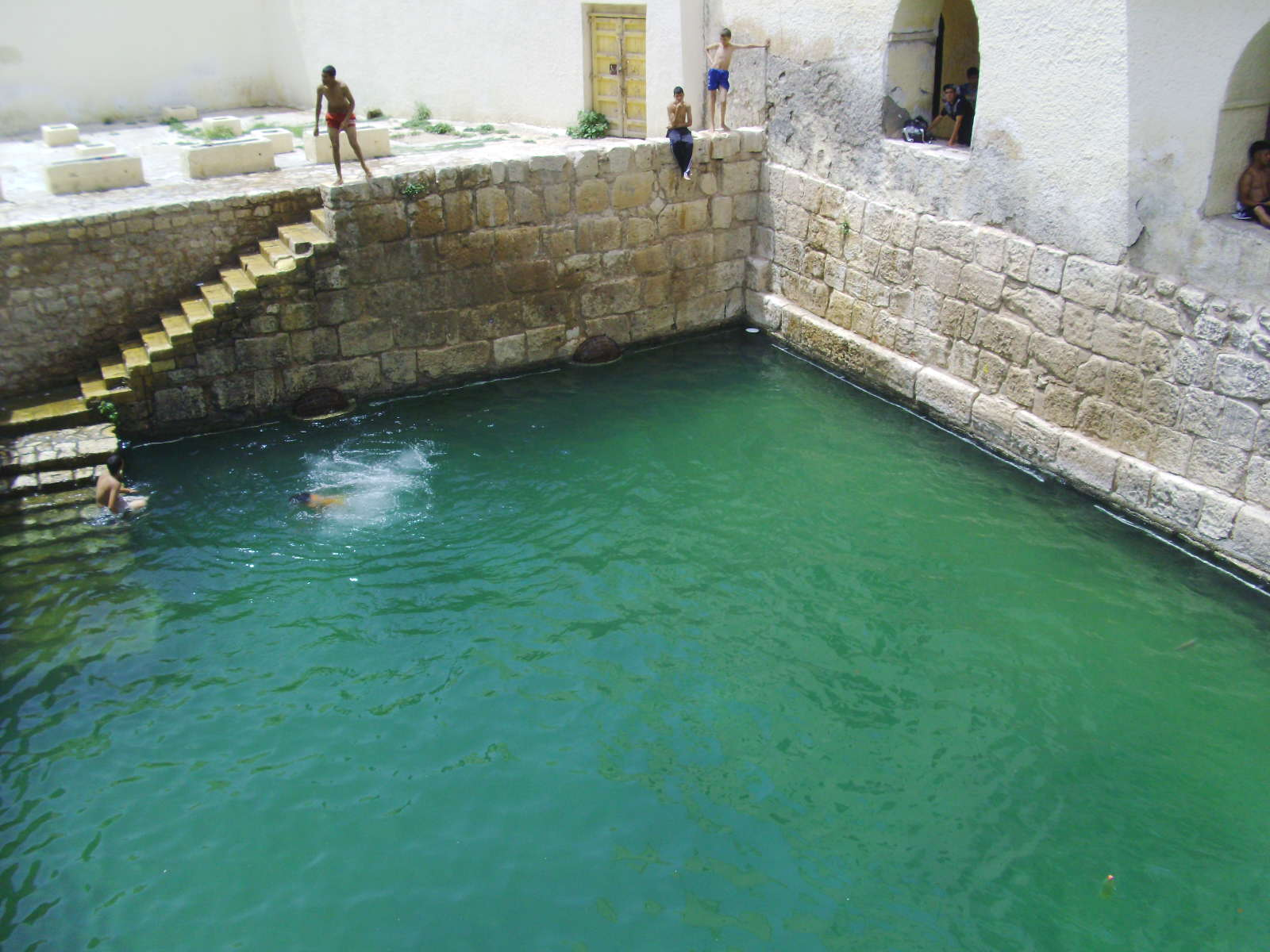

Beyond their architectural significance, the Roman pools of Gafsa hold immense cultural and historical importance for the region. In ancient times, these thermal baths served as communal gathering spaces where people from all walks of life would converge to socialize, relax, and rejuvenate. The therapeutic properties of the hot springs were believed to possess healing properties, attracting visitors seeking relief from various ailments and ailments. Additionally, the pools likely played a role in religious rituals and ceremonies, serving as sacred sites where worshippers could commune with the divine while immersed in the soothing waters.
Preservation and Archaeological Insights
Today, the Roman pools of Gafsa stand as poignant reminders of Tunisia’s rich archaeological heritage, attracting visitors from around the world eager to explore their storied past. Through ongoing preservation efforts and archaeological excavations, scholars continue to uncover new insights into the construction techniques, hydrological systems, and cultural practices associated with these ancient structures. Each discovery adds to our understanding of Roman life in North Africa and contributes to the broader field of classical archaeology. As stewards of this cultural legacy, it is our responsibility to safeguard and celebrate the Roman pools of Gafsa for generations to come.