Coins have long been a fascinating aspect of archaeology, providing valuable insights into ancient economies, trade routes, and political systems. Throughout history, coins have served as essential tools for commerce and communication, circulating far and wide across empires and civilizations. Archaeologists have uncovered numerous archaeological sites where ancient coins were found, offering a window into the past and enriching our understanding of ancient societies. In this blog post, we will explore the top five archaeological sites where remarkable discoveries of ancient coins have been made.
1. Pompeii, Italy: Preserved by Vesuvius’s Fury
Pompeii, the ancient Roman city famously buried by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, has yielded an abundance of archaeological treasures, including a significant number of ancient coins. Excavations at Pompeii have unearthed coins from various periods of Roman history, providing valuable insights into the city’s economic and social life before its tragic destruction. These coins offer clues about trade networks, taxation, and the daily lives of Pompeii’s inhabitants.

2. Ephesus, Turkey: Gateway to the Ancient World
Ephesus, an ancient Greek and Roman city located on the coast of present-day Turkey, was once a bustling metropolis and a hub of trade and commerce in the Eastern Mediterranean. Excavations at Ephesus have revealed numerous ancient coins dating back to the Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine periods. These coins bear witness to the city’s importance as a center of trade and culture and shed light on its interactions with other civilizations in the region.
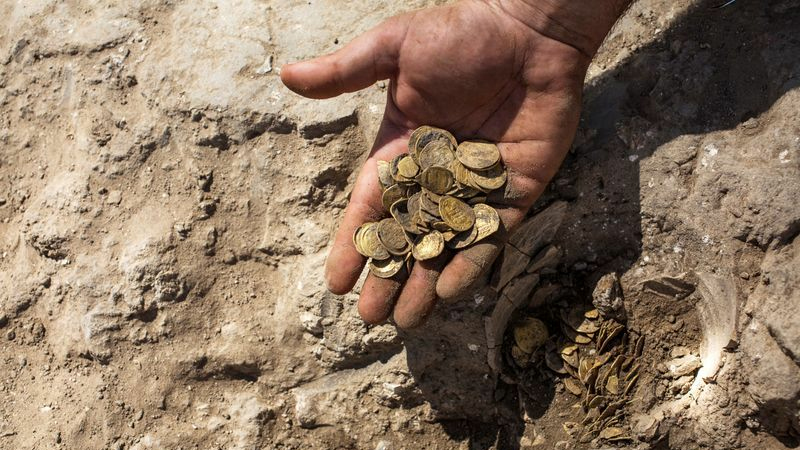

3. Athens, Greece: Cradle of Democracy and Coinage
Athens, the capital of Greece and one of the oldest cities in the world, holds a special place in the history of coinage. The ancient Athenians were pioneers in the development of coinage as a medium of exchange, producing some of the earliest coins in the Western world. Archaeological excavations in Athens have uncovered a wealth of ancient coins, including the iconic “owls” of Athens, which were minted from the 6th to the 4th centuries BC. These coins are not only artifacts of ancient commerce but also symbols of Athenian democracy and cultural achievement.

4. Troy, Turkey: Myth and Reality
Troy, the legendary city immortalized in Homer’s epic poems, has been the subject of archaeological exploration for centuries. Excavations at the site of Troy have revealed a trove of ancient artifacts, including coins from various periods of the city’s history. These coins provide valuable evidence of Troy’s existence as a real ancient city and offer insights into its economic and cultural connections with other civilizations in the region.
5. Colchester, England: Roman Britain’s First City
Colchester, located in the county of Essex, England, was once the capital of Roman Britain and one of the most important cities in Roman-occupied territory. Archaeological excavations in Colchester have uncovered a wealth of ancient coins, reflecting the city’s role as a center of trade and administration in Roman Britain. These coins provide valuable insights into the economy and society of Roman Britain and the interactions between Romans and native Britons.
Unlocking the Past Through Ancient Coins
In conclusion, ancient coins are not just pieces of metal but windows into the past, offering glimpses of ancient economies, political systems, and cultural interactions. The top five archaeological sites mentioned in this blog post—Pompeii, Ephesus, Athens, Troy, and Colchester—have all yielded significant discoveries of ancient coins, enriching our understanding of ancient civilizations and their contributions to human history. As archaeologists continue to uncover new archaeological sites and make exciting discoveries, ancient coins will remain valuable tools for unlocking the mysteries of the past and illuminating the stories of ancient peoples and cultures.