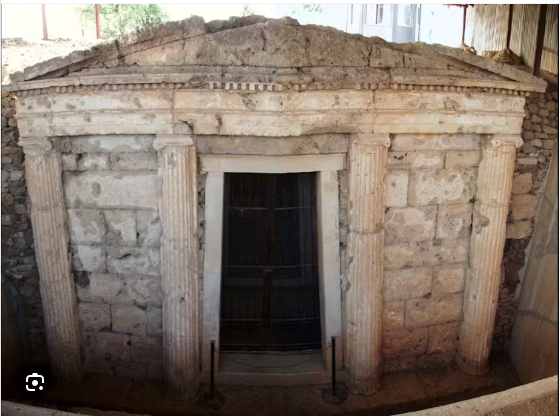
A Journey Through Time
Nestled amidst the picturesque landscapes of Macedonia, Greece, lies a hidden gem of ancient architecture—the Macedonian tomb of Ptolemaïs. Dating back to the 2nd century BC, this remarkable funerary monument offers a tantalizing glimpse into the rich history and culture of the region. With its distinctive Doric facade and two chambers, the tomb stands as a testament to the craftsmanship and ingenuity of its builders, inviting us to embark on a journey through the ancient past.
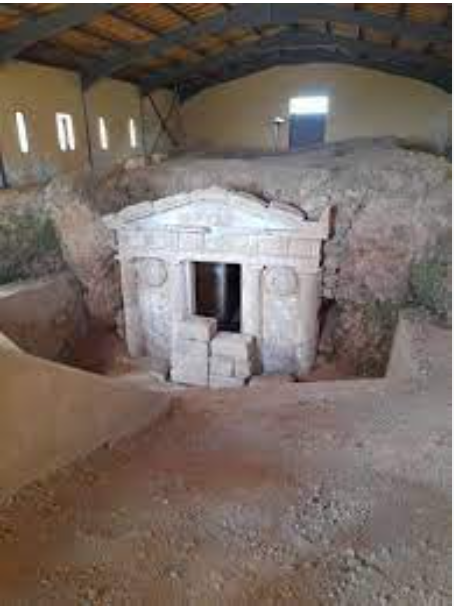

The Architectural Marvel
The Macedonian tomb of Ptolemaïs is distinguished by its imposing Doric facade, which reflects the architectural style prevalent during the Hellenistic period. Carved from local limestone, the facade features intricately detailed columns and pediments, evoking a sense of grandeur and solemnity. Beyond the facade, the tomb comprises two chambers—a main chamber and a smaller antechamber—where the remains of the deceased were interred. The interior walls of the chambers were often adorned with frescoes and reliefs, depicting scenes from daily life, mythology, or funerary rituals.
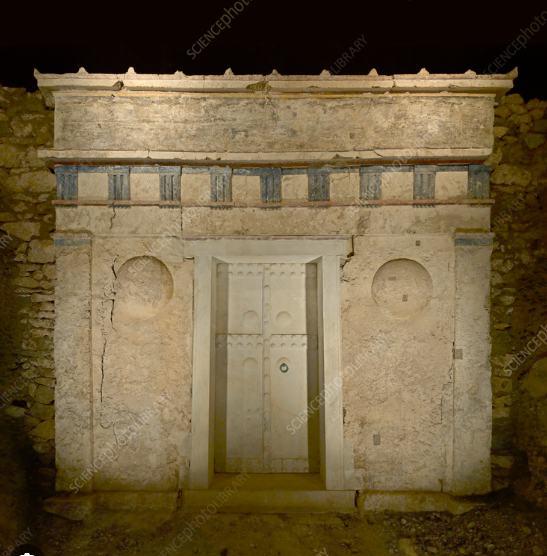

The Historical Significance
Ptolemaïs, the site of the Macedonian tomb, was an ancient city of considerable importance during the Hellenistic and Roman periods. Founded by the successors of Alexander the Great, Ptolemaïs served as a thriving center of trade, culture, and religion. The discovery of the tomb not only sheds light on the funerary practices of the ancient Macedonians but also provides valuable insights into the social structure and beliefs of the time. As a final resting place for the elite members of society, the tomb symbolizes the reverence and respect accorded to the deceased in ancient Macedonian culture.As visitors approach the tomb, they are greeted by the majestic sight of this ancient monument, evoking a sense of awe and reverence. Beyond its exterior beauty, the tomb’s two chambers beckon explorers to venture inside and uncover the secrets that lie within.

Preserving the Legacy
Today, the Macedonian tomb of Ptolemaïs stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of the ancient world. Despite the passage of centuries, the tomb’s Doric facade remains remarkably intact, serving as a poignant reminder of the ingenuity and artistry of its creators. Archaeological excavations have revealed a treasure trove of artifacts and archaeological finds within the tomb, offering valuable clues about the lives and customs of its inhabitants. Through careful preservation and conservation efforts, the Macedonian tomb continues to inspire and educate visitors from around the world, providing a window into the past and a glimpse of the mysteries that lie buried beneath the earth.
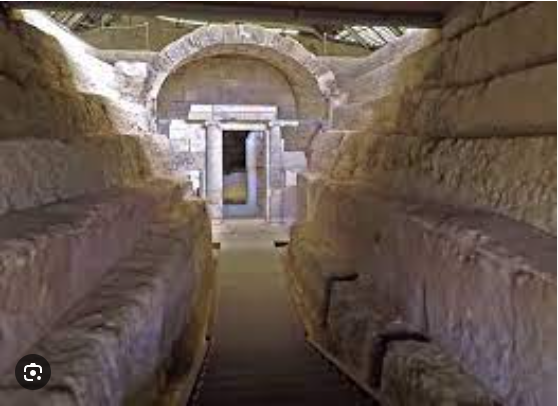

Discovering Ancient Wonders
As we reflect on the splendor of the Macedonian tomb of Ptolemaïs, we are reminded of the enduring allure of ancient discoveries and the rich tapestry of human history. From its Doric facade to its sacred chambers, the tomb stands as a testament to the ingenuity, creativity, and spirituality of the ancient Macedonians. As we marvel at its architectural beauty and historical significance, let us also celebrate the ongoing efforts to preserve and protect our cultural heritage for future generations to cherish and explore. And as we continue to unearth the secrets of the past, let us remain open to the wonders that await us, eager to uncover the mysteries that lie hidden beneath the sands of time.

As we reflect on the enduring legacy of this remarkable monument, let us also celebrate the ongoing discoveries and advancements in the field of archaeology, which continue to shed light on the mysteries of ancient civilizations. And as we marvel at the wonders of the Macedonian tomb, let us remain open to the endless possibilities of ancient discoveries, eager to uncover the secrets that lie buried beneath the sands of time.